-
ACCIONA has built over 5,000 kilometers of highways, motorways and roads all over the world in recent years: a veritable Mappa Mundi of smart roads, increasingly innovative and sustainable, thanks to the advances in the technological revolution.
-
If the Roman Empire excelled in anything, it was a genius for public works. Its roads were the first ever. When you travel from Italy or the south of France to Spain, for example, the highway states that on some sections you are using the old Roman route. Its legacy is alive.
Roman governors soon realized the importance of creating a road network over their territories. And, in the Empire, road construction was always a matter that was directly overseen by successive Emperors or their immediate deputies.
Roman roads could also be said to be the first smart roads in that their construction techniques applied all the technology available to them and the engineering concepts they used were incredible for their time. They took into account resistance to movement on gradients and longitudinal slope, never greater than the 8% over which animal-drawn carriages could transport cargo. When necessary, the Romans levelled land to the millimeter, calculated according to the hardness of the mountain rock, and they used a collection of solid, smart materials to transport heavy items at speed. They also had accurate signage.
All kinds of goods and materials were transported over Roman roads, from Turkish marble to Andalusian olive oil, gold, lead, cereals, etc. Both armies and citizen travelers moved by them. Many high-ranking Romans, who knew by which routes people traveled, chose to be buried at privileged locations next to the roads that ensured passers-by leaving and entering Rome would visit their tombs. “I am next to the road, thus powerful,” they seemed to be saying. Everyone was aware of the importance of a road network that linked territories, trade, the economy and communications over a large part of Europe and Asia.
-
-
Engineering has changed a lot since the Romans taught the world how to build infrastructure. But one reality hasn’t changed in the intervening years: the power of roads to stimulate the economy and underpin society’s progress. Roads convert far into near, difficult into easier, and the impossible is allowed to happen.
ACCIONA has built over 5,000 kilometers of highways, motorways and roads all over the world in recent years: Australia, Spain, Canadá, Denmark, and so on; a veritable Mappa Mundi of smart roads, increasingly innovative and sustainable, thanks to the advances in the technological revolution. It also carries out maintenance on a multitude of roads, including cleaning and clearing of scrub, drainage networks, culverts, underdrains and signage works.
-
Roads stimulate the economy and underpin society’s progress.
-
-
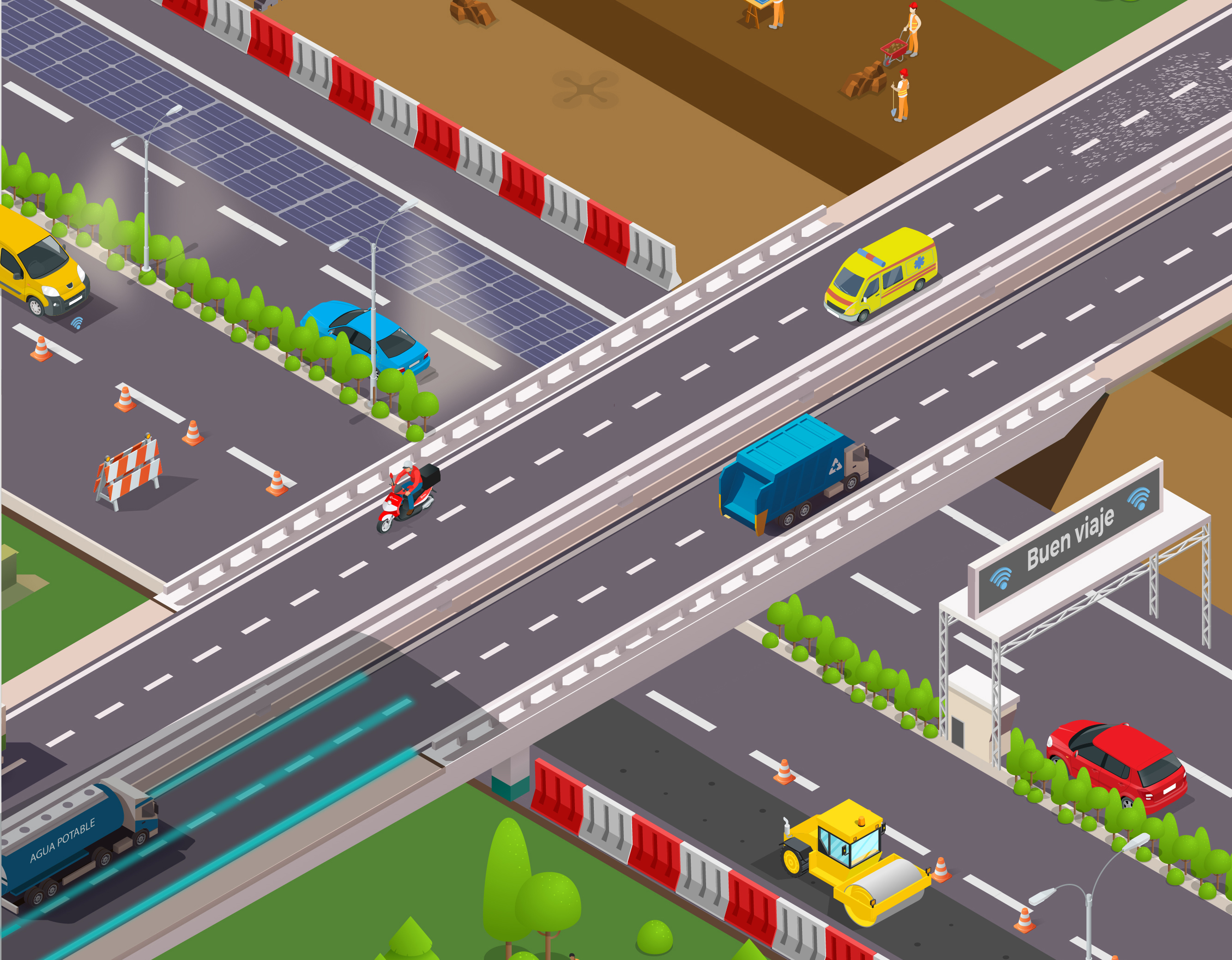
SMART ROADS: COCKTAIL OF TECHNOLOGIES
Today these highways and roads emerge on the screen of engineers in ACCIONA’s centres for technological innovation with the help of sophisticated software. Later, they are made real in the remotest of places thanks to the new applications of topography, 3D and 4D modeling, sensor systems, remotely operated machinery, drones, laser scanning and smart and sustainable materials capable of self-repair and which warn about where they are deteriorating. Solutions that pursue the application of the concept of circular economy and digitize processes to reduce construction delays and increase the reliability and safety of construction projects.
Another of the most important tasks for our engineers is driver safety. Thanks to advances in innovation and sustainability, ACCIONA’s road projects are essential not only in reducing CO2 emissions to the atmosphere but also the number of accidents on the road.
BUILDING WITH THE ENVIRONMENT IN MIND
But when designing a smart highway, engineers must also consider what damage it might cause. ACCIONA prioritizes environmental studies in the development of road projects so that a minimum of impact is generated on the surroundings and transport emissions can be reduced. Examples are designing routes that harmonize the speed of vehicles, avoiding driving in low gears and hard braking, toll points without barriers and using wireless communications so that cars don’t have to stop and queue, a big cause of pollution.
Additionally, the stages of damage prevention and conservation in the places in which we work include the tasks of rehabilitating surrounding landscapes through the planting of trees and shrubs, the creation of new landscapes to reduce environmental impact and respect for vegetation, animal life and cultural heritage in the vicinities.
-

-
ACCIONA’S FLAGSHIP HIGHWAYS AND SMART ROADS
ACCIONA’s experience can be appreciated by its network of over 5,000 km of highways and roads built worldwide. These are some of the most important smart roads:
- ROSKILDE FJORD HIGHWAY (DENMARK): the 8.6 km-long road designed and built by ACCIONA is located in one of the most beautiful spots in Denmark. In fact, protection of the environment and the species living there was one of the project’s highest priorities. The route offers an alternative access to the city of Frederikssund, with a spectacular 1-km concrete bridge with 16 pillars crossing Roskilde Fjord to connect its east and west banks. The construction project, delivered three months early, will improve communications in the region and alleviate traffic congestion in Frederikssund.
- A-14 FROM A CORUÑA (SPAIN): more than 25,000 vehicles a day take this route out of the Galician city of A Coruña, a road which received the 2017 award for Galicia’s Best Engineering Work for its quality and contribution toward social, environmental and economic improvements in the region. Smaller districts are better communicated now, thanks to the smart road. The work involved planting 5,700 trees and 13,000 shrubs. The section between As Lonzas and A Zapateira was particularly demanding due to its difficult terrain.
-
- PACIFIC HIGHWAY (AUSTRALIA): ACCIONA was responsible for the construction project of the 19.5-kilometer section between Warrell Creek and Nambucca Heads. The project included several longitudinal bridges over Upper Warrell Creek, Williamson Creek and Warrell Creek, and the Nambucca flood plain and river.
- PUHOI-WARKWORTH HIGHWAY (NEW ZEALAND): the 18.5 km of four-lane highway from the Johnstone Hills tunnels north of Warkworth are strategic for the country’s transport network. The highway built by ACCIONA will connect the north of New Zealand with the triangle that forms the cities of Auckland, Walkato and Tauranga.
- A-30 HIGHWAY, QUEBEC (CANADA): ACCIONA designed, built and operates the new 42-km stretch of this highway, which crosses Montreal’s southern coastal region. Six million vehicles a year use this smart highway, which has shortened journeys, reduced congestion and lowered CO2 emissions, leading to cleaner air and, at the time of its construction, the second longest incrementally launched bridge in the world, Beauharnois bridge. This construction project was a challenge due to the area’s weather, with temperatures of -15° C and up to 20 cm of snow.
-
Hit the question
How many kilometers of highways, motorways and roads has ACCIONA built?
-
-
Bringing the coast back to life
La Chira wastewater treatment plant, built and operated by ACCIONA, serves 2.5 million inhabitants in Lima and contributes to the environmental, economic and social regeneration of the city
-
-
-